Hello, I am Hoon-dong Park, CEO of HELP PLUS Administrative Attorney. We are a legal visa agency authorized by the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Korea to handle administrative tasks related to foreign nationals’ entry, stay, and departure in Korea. We are known as the ‘Visa Meister.’
‘Meister’ is a German word meaning ‘Master’ in English, and because I hold not only a general administrative license but also a certified German translation administrative license, I am fond of the nickname ‘Visa Meister.’
As an official partner of DIOKOS, Visa Meister aims to introduce Korea’s visa stories in an easy-to-understand way for foreigners through the renowned ‘KoreaAgain’ website. If you have any questions or need assistance with visa changes or upgrades in Korea, feel free to contact us at any time.
Types of Korean Visas: Over 300 Types
Today, I will introduce the various types of visas in Korea. There are over 300 visa types in Korea. Of course, you don’t need to know all of them.
Each visa code begins with one of eight letters, ranging from A to H. Here’s a breakdown:
A
- Diplomacy (A-1)
- Public Service (A-2)
- Agreement (A-3)
B
- Visa Exemption (B-1)
- Transit (B-2)
C
- Short-Term Visit (C-3)
- Short-Term Employment (C-4)
D
- Cultural Arts (D-1)
- Study Abroad (D-2)
- Technical Training (D-3)
- General Training (D-4)
- Journalism (D-5)
- Religion (D-6)
- Resident Employee (D-7)
- Trade Investment (D-8)
- Trade Management (D-9)
- Job Seeker (D-10)
E
- Professor (E-1)
- Conversation Instructor (E-2)
- Research (E-3)
- Technical Guidance (E-4)
- Professional Employment (E-5)
- Entertainment (E-6)
- Specific Activities (E-7)
- Seasonal Worker (E-8)
- Non-Professional Employment (E-9)
- Seaman Employment (E-10)
F
- Visiting Family (F-1)
- Residency (F-2)
- Accompanying Family (F-3)
- Overseas Koreans (F-4)
- Permanent Residency (F-5)
- Marriage Immigrant (F-6)
G
- Refugees, etc. (G-1)
H
- Working Holiday (H-1)
- Visiting Employment (H-2)
A
- 외교(A-1)
- 공무(A-2)
- 협정(A-3)
B
- 사증면제(B-1)
- 통과(B-2)
C
- 단기방문(C-3)
- 단기취업(C-4)
D
- 문화예술(D-1)
- 유학(D-2)
- 기술연수(D-3)
- 일반연수(D-4)
- 취재(D-5)
- 종교(D-6)
- 주재(D-7)
- 무역투자(D-8)
- 무역경영(D-9)
- 구직(D-10)
E
- 교수(E-1)
- 회화지도(E-2)
- 연구(E-3)
- 기술지도(E-4)
- 전문직(E-5)
- 예술흥행(E-6)
- 특정활동(E-7)
- 계절근로(E-8)
- 비전문취업(E-9)
- 선원취업(E-10)
F
- 방문동거(F-1)
- 거주(F-2)
- 동반(F-3)
- 동포(F-4)
- 영주(F-5)
- 결혼이민(F-6)
G
- 난민 등(G-1)
H
- 관광취업(H-1)
- 방문취업(H-2)
Among these, the most popular visas for foreign nationals are usually the D, E, and F categories. This is because they allow for long-term stays of over 90 days, legal employment, and the issuance of an Alien Registration Card (ARC). I will focus on these categories in future explanations.
Visa Application Methods: 3 Types
There are three main ways for foreign nationals to apply for a Korean visa. Here, visa, sojourn status, and permission to stay all have the same meaning. Overseas, Korean embassies (consulates) tend to use the terms ‘visa’ or ‘sojourn status,’ while in Korea, ‘sojourn status’ is more commonly used.
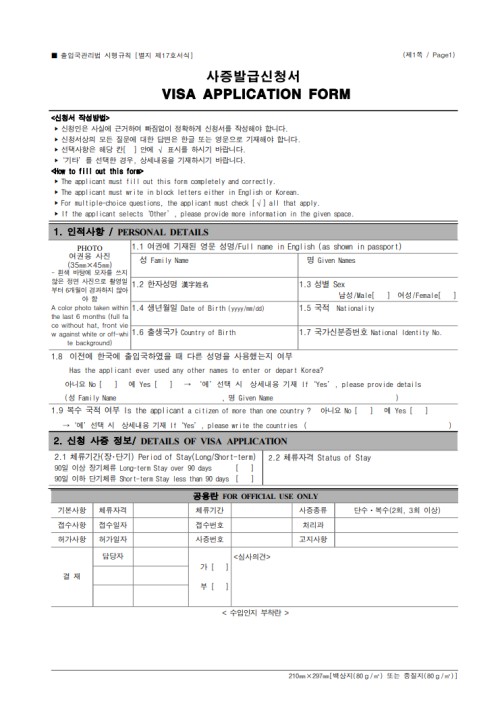
VISA Application Form:
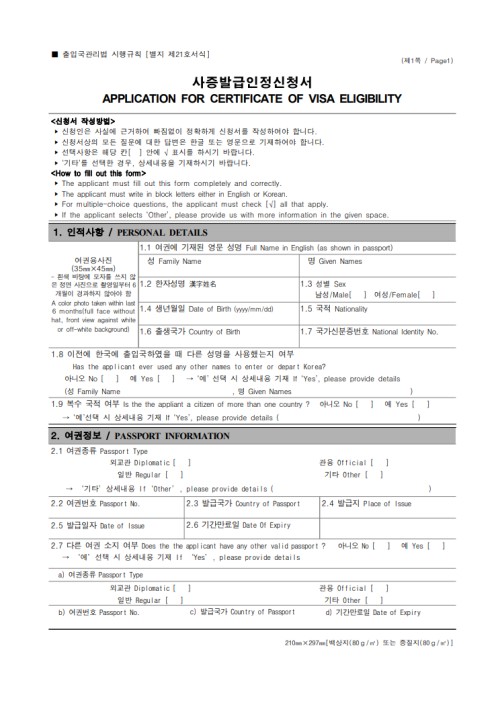
This method is for foreigners outside of Korea who wish to enter the country. They must visit a Korean embassy or consulate in their country and submit a ‘VISA Application Form.’ The Consul General may issue short-term and family visas.Application for Certificate of VISA Eligibility:
Before the Korean consulate issues a visa, the Korean Immigration Office first reviews the application and decides whether to grant it. For example, if Company A in Korea wants to hire foreigner C from Country B, Company A must apply for a Certificate of VISA Eligibility at the Immigration Office and obtain approval.Change of Sojourn Status:
A foreigner already in Korea who wishes to change their current sojourn status must apply for a status change. The most important factor here is whether the applicant meets the requirements for the change. If the legal requirements are not met, the status change will be denied.
Application Forms: 3 Types
Just as there are three types of visa applications, there are also three types of application forms. For overseas applications, the VISA Application Form is used. In Korea, the Application for Certificate of VISA Eligibility is used, and for changes of sojourn status, the Application Form (Report Form) is required.

That concludes today’s explanation of the types of Korean visas and how to apply for them. If you have any further questions or need assistance, please contact HELP PLUS Administrative Attorney, the ‘Visa Meister’ for foreigners in Korea. Thank you!
- https://blog.naver.com/celloberlin
- Kakao : phdcelloberlin
- Whatsapp : + 82 10-3174-3793
- celloberlin@naver.com